Bookkeeping vs Accounting: Understanding the Differences
By: Jenn Hall | April 2025
Bookkeeping and accounting are related financial careers, but their functions, salary expectations, career trajectory, and even the training needed to get started will differ. Both roles support the financial integrity and health of a business, but in different ways. To better understand these roles and the steps needed to begin a career in each, we’ve outlined some key career details so you can easily see the differences and better determine whether one of these careers is right for you.
The difference between bookkeeping and accounting is that bookkeepers keep detailed financial records of a company’s earnings and expenses, while an accountant uses that information to help a company make financial decisions for the future. In short, a bookkeeper will compile data for an accountant to use. However, those aren’t always the only differences.
Bookkeeping vs accounting: Job titles
Individuals pursuing a career in bookkeeping can expect their title to be bookkeeper, bookkeeping clerk, accounting specialist, accounting clerk, or auditing clerk. Although these titles differ, the role behind the title is generally the same.
In contrast, individuals seeking a career in accounting may find themselves with a professional title as government accountant, management accountant, public accountant, external auditor, internal auditor, or IT auditor. These titles reflect some nuanced specialties (e.g., auditors will review data and sources for accuracy and usability, accountants will review, analyze, and interpret financial data for accuracy and usability).
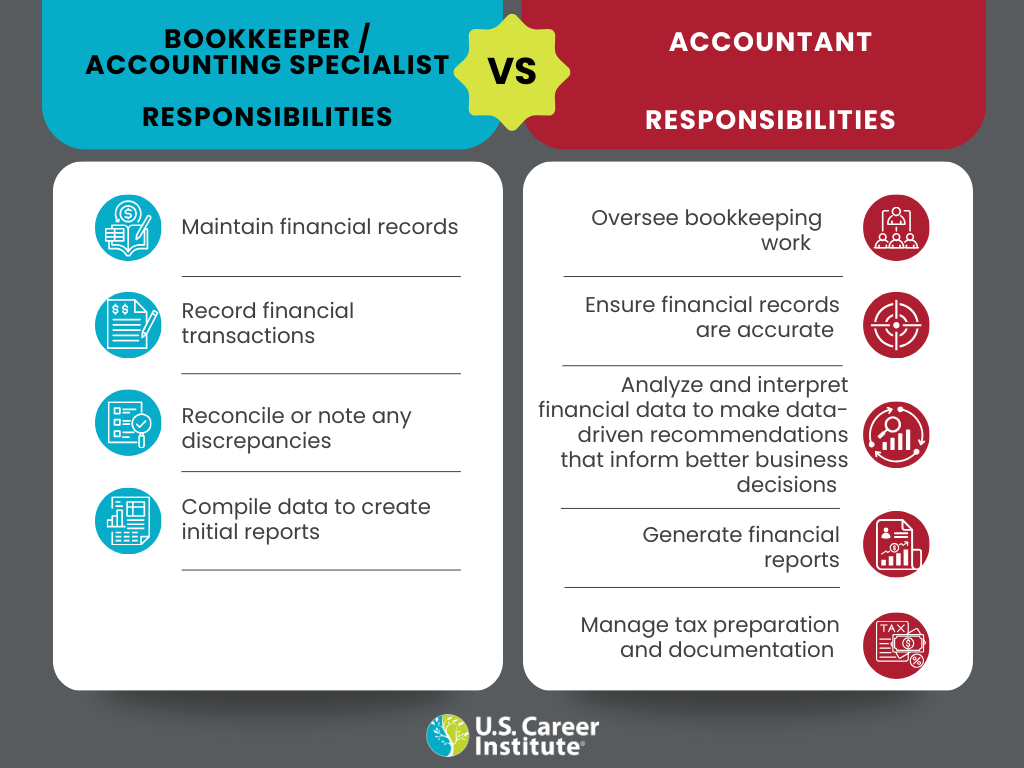
Bookkeeping vs accounting: Primary responsibilities
Although bookkeepers and accounting professionals both work with financial records, their approach and levels of responsibility are different. For example, a bookkeeper is responsible for maintaining detailed financial records of an organization’s day-to-day transactions, whereas an accountant will analyze those records to make or advise on data-driven business decisions.
Bookkeeping vs accounting: Job outlook
Understanding the projected job growth for a career path can help individuals set appropriate expectations for the volume of prospective job opportunities after completing any required education or training. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Bookkeeping roles are expected to see a decline of 5% through 2033. Although there is a decline, job opportunities are still available with 174,900 new job openings projected each year, on average.
Accountant positions, on the other hand, are expected to grow at 6% through 2033, which is faster than average for all occupations. Additionally, an average of about 130,800 job openings for accountants are expected each year.
Bookkeeping vs accounting: Salary expectations
Salary expectations are based on a variety of factors, including location, education, years of experience, industry or business type, and certification. That said, the current median annual salary for a bookkeeper is $47,440, or $81,680 for an accountant.
Some accountants will choose to pursue their industry credentials as a certified public accountant (CPA), which will influence their earning potential. According to Salary.com, accountants who have earned their CPA can earn anywhere between $70,235 and $461,014, as of April 2025.
It’s not uncommon for individuals to begin their careers as a bookkeeper with the intention of advancing their career to accountant or even CPA. This is a great steppingstone approach, not only to gain valuable skills and experience, but also to gradually increase earning potential.
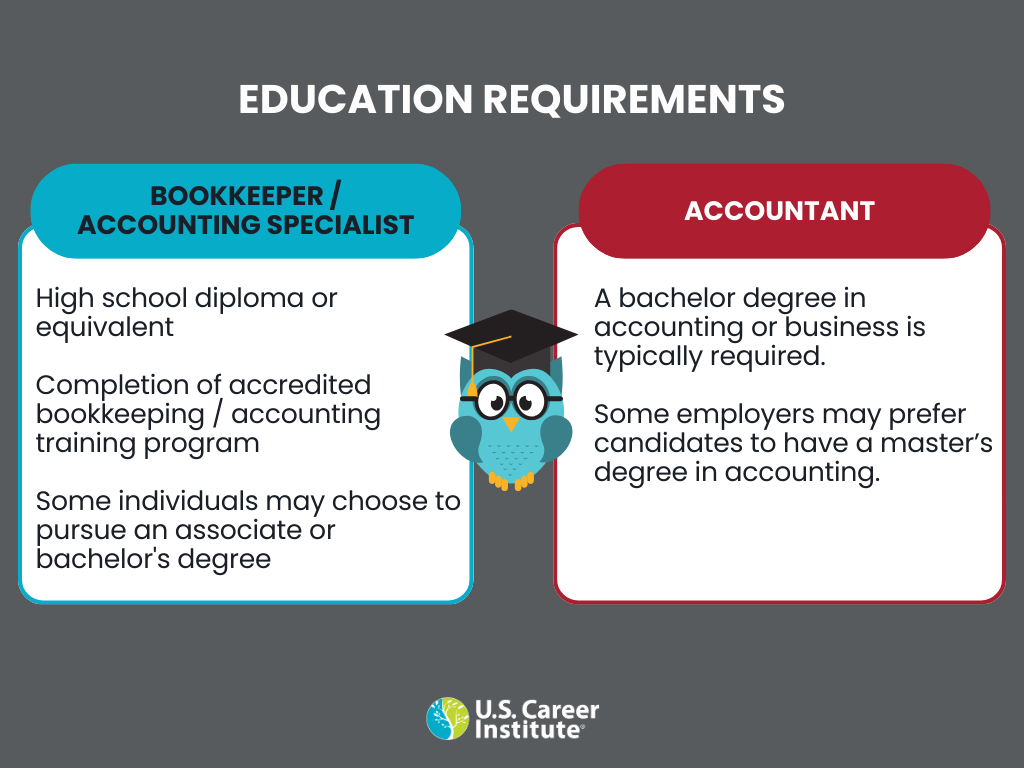
Bookkeeping vs accounting: Education and training
Bookkeepers and accountants work directly with sensitive financial data, which requires both formal and on-the-job training. To break this down further:
Helpful resources:
- Online high school program
- Online bookkeeping certificate program
- Online accounting services specialist certificate program
- Online accounting associate degree program
Bookkeeping vs accounting: License and industry certification
A state license is not required to practice as a bookkeeper or accountant, but many employers will either prefer or require individuals to have an industry certification.
Industry certification for bookkeeping is not required, but it may be preferred. Industry credentials can help showcase knowledge and skills, giving individuals a competitive edge in the job market. Some common certifications may include:
There are several potential industry certifications that accountants may pursue, including:
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA)
- Certified Government Financial Manager (CGFM)
- Certified Management Accountant (CMA)
- Certified Internal Auditor (CIA)
This is not an exhaustive list, but does show some of the potential areas of focus that an accountant may choose to pursue.
Not only can an industry certification demonstrate an individual’s level of knowledge and expertise within a specified area, but it also can influence salary potential and help candidates stand out to prospective employers. This is true for both bookkeeping and accounting career paths.
How to become a bookkeeper or accountant
For those who love working with numbers and are interested in the nitty-gritty financial aspects of a business, a career as a bookkeeper or an accountant may be the perfect opportunity.

Ready to start with step 1 on your journey toward becoming a bookkeeper or accountant? U.S. Career Institute can help. Whether you need to earn your high school diploma first or are ready to jump right in to a certificate or degree program, we’ve got you covered with 100% online, self-paced, and DEAC accredited education. Enroll today or speak with an admissions representative to discuss your career goals so you can choose the best program to meet them.
