How to Become a Medical Assistant
By: Jenn Hall
Updated January 2025
There are several roads that lead to a fulfilling career in healthcare, including one that enables you to begin your career as a medical assistant. With both clinical and administrative responsibilities, medical assistants have the unique opportunity to support both patients and providers. For those entering the field as a medical assistant, the timing could not be better. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates a 15% growth in the medical assistant career through 2033, with nearly 120k new job openings projected each year.
Primary responsibilities of a Medical Assistant

A medical assistant may handle a variety of clinical and administrative tasks throughout their day. For example, some of their primary responsibilities may include:
- Taking medical histories
- Explaining treatment procedures to patients
- Preparing patients for examinations
- Assisting the physician during examinations
- Collecting and preparing laboratory specimens
- Answering telephones
- Greeting patients
- Updating and filing patient medical records
- Scheduling appointments
Medical assistants also may choose to focus on a healthcare specialty (e.g., pediatrics) within their career, which may affect some of their daily responsibilities.
Beyond the core tasks and responsibilities, there are some desirable qualities and skills that medical assistants should have or strive to attain, such as:
- Communication
- Empathy and compassion
- Attention to detail
- Organization
- Time management
- Ability to multi-task
- Computer skills
Salary potential of a medical assistant in the U.S.
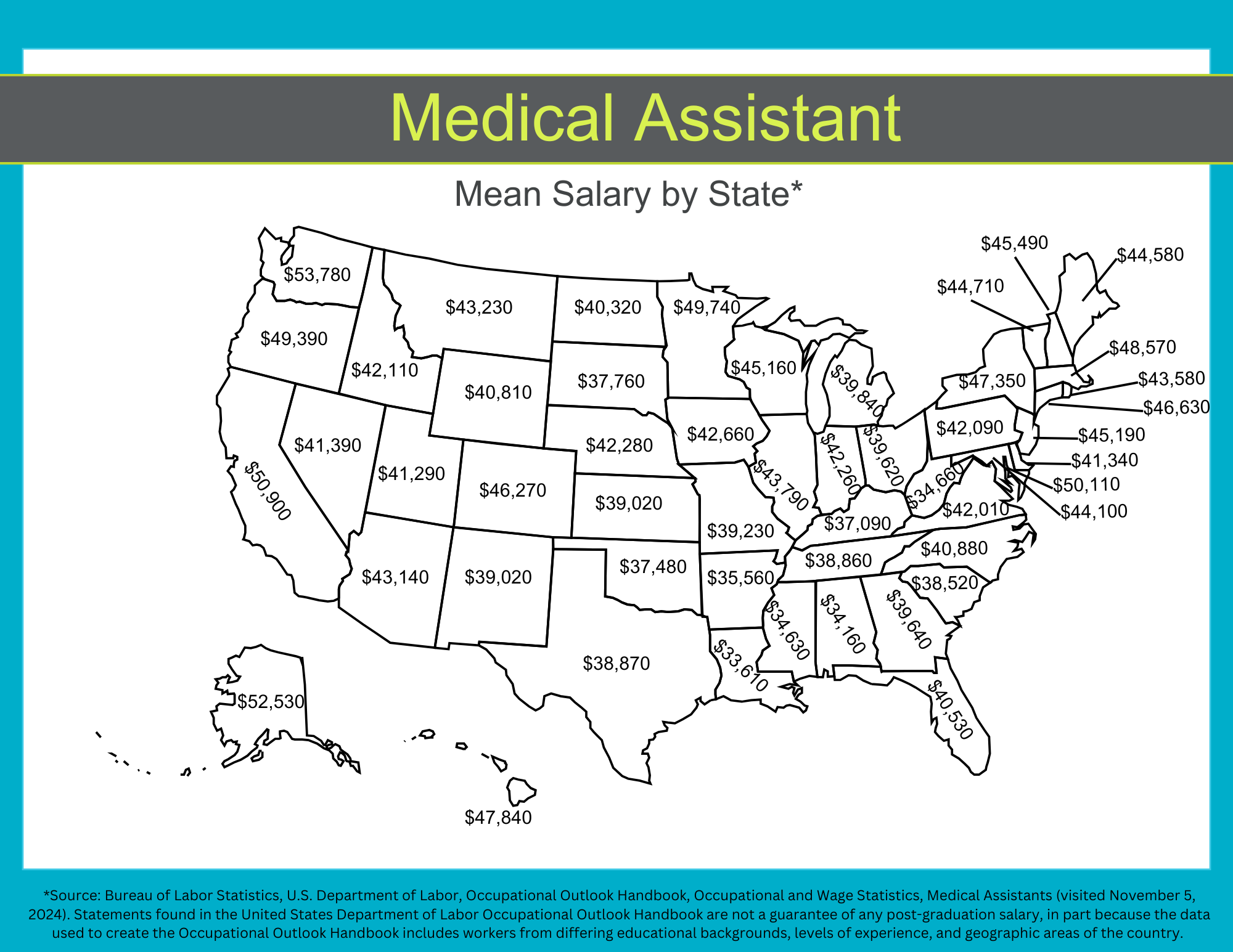
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for a medical assistant is $42,000. While this is a helpful baseline, it’s not the full story. There are several factors that can influence your earning potential as a medical assistant, including location, facility type, specialty, education, certification, and years of experience.
For example, a medical assistant working within a hospital may earn $44,350, while a medical assistant working at a physician’s office may earn $40,670. Additionally, salary ranges vary by geographic location, accounting for the cost of living and other factors (see map below).
Steps to become a Medical Assistant
Does the idea of becoming a medical assistant excite you, but you’re unsure where to start? Don’t worry; the process is much simpler than you may realize.
- Earn your high school diploma. Entry-level medical assistant positions typically require a high school diploma as the minimum educational requirement.
- Gain targeted career education and skills in medical assistant. Many employers also seek candidates who have formal training or experience as a medical assistant, ensuring they have familiarity with medical terminology and medical office processes and procedures. To gain the desired knowledge and skills, many future medical assistants choose to earn a professional certificate or associate’s degree through U.S. Career Institute.)
- Washington residents only: Attain a Medical Assistant license. Currently, Washington is the only state that requires a license in one of four categories to practice as a medical assistant.
Beyond initial career training, some professionals may choose (or are required) to pursue industry certification, such as a Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA), Certified Medical Administrative Assistant (CMAA), or others. U.S. Career Institute’s Medical Assistant certificate and associate degree programs prepare students to pursue the CCMA and/or CMAA certification, with the cost of the exam and exam preparation materials included in the tuition. Graduates from U.S. Career Institute’s Medical Assistant programs pass the CCMA certification exam and CMAA certification exams at a higher rate than the national average.
Although certification is not required in all circumstances, it can be beneficial to further demonstrate your knowledge and competency to current or future employers.
What's next?
If you’re ready to begin your journey toward a fulfilling career as a medical assistant, the first step is to seek out high-quality education. Whether that means finishing your high school education or getting started with medical assistant career training, U.S. Career Insititute can help you achieve your goals.
Ready to get started? Learn more about our online medical assistant program and get started today!
